Problem Set questions appear in black, and Answers appear in this magenta color.
1. How many file systems does Windows NT 3.51 support, and what are they?
2. Up to how many characters can be used to name a file on a FAT file system through Windows NT? And under DOS?
3. Up to how many characters can be used to name a file on a HPFS file system through Windows NT?
4. Up to how many characters can be used to name a file on a NTFS file system through Windows NT?
5. What does the FAT acronym represent?
6. What operating systems can see and use HPFS? What does the HPFS acronym represent?
7. What operating systems can see and use NTFS? What does the NTFS acronym represent?
8. Does FAT preserve case of filenames under NT? How about under DOS?
9. Does NTFS preserve case of filenames?
10. What is the maximum FAT partition size under Windows NT?
11. What is the maximum theoretical HPFS partition size under Windows NT?
12. Of the choices below, what are the true statements about NTFS?
13. What is the maximum file and partition size under NTFS? How many megabytes is this?
14. Of the following, which is the correct command-line syntax to convert a FAT partition to NTFS?
15. If Windows NT cannot gain exclusive access to the drive that you want to convert, which of the following happens?
16. Of the following, which is the likely generated 8.3 alias for this long filename: "PCC Windows NT Class.TXT"
17. What file attributes does a long filename have on a FAT partition?
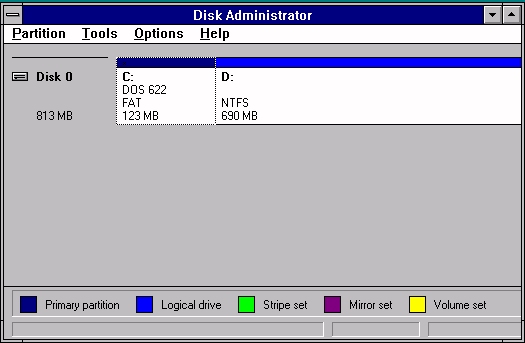
18. On a Windows NT Workstation, someone started Disk Administrator and saw this (continued below graphic)

a. Which partition or partitions can be marked active?
- Only Partition C can be marked as active. Partition D is not a primary partition, and thus cannot be marked as active.
b. What are the file systems in use on this Windows NT Workstation?
- FAT and NTFS
c. How large (in megabytes) is each partition?
- 123 MB on the FAT partition and 690 MB on the NTFS partition.
d. What is the volume label name for each partition?
- Partition C is named "DOS 622" and Partition D is not named.
e. Is Disk 0 a SCSI or an IDE hard-disk?
- This information cannot be determined with Disk Administrator.
19. What is the maximum number of primary partitions a single hard-disk can contain?
20. What is the maximum number of extended partitions a single hard-disk can contain?
21. Volume sets and Stripe sets are initially created from:
22. Which of the following cannot be performed on a Windows NT Workstation:
23. User Racer-X has 3 hard-disks on his Windows NT Workstation. The free areas on each of the three disks are 150 MB, 200 MB, and 75 MB in size respectively. For each configuration below, what can Racer-X do?
a. Racer-X wants to create a volume set. What is the largest size volume set he can create?
- 425 MB
b. Racer-X wants to create a stripe set. What is the largest stripe he can create using any combination of the drives?
- 300 MB
24. User Trixi has a Windows NT Workstation identical to Racer-X's. She also has 150, 200, and 75 megabytes of free space on her three hard-disks.
a. What is the smallest stripe set she can create using any combination of the drives, but using all the free space from any drive she chooses to have in her combination?
- 150 MB
b. What is the largest stripe set she can create using all the drives?
- 225 MB