Problem Set questions appear in black, and Answers appear in this magenta color.
1. Of the following types of disk partitions that can be used with Windows NT, which support local file & directory security?
2. Name one condition that a user needs to have in order to set permissions for a file or directory.
At least one of the three following conditions must be met:
- The user has Full Control access to the file or directory
- The user has Change Permission permission
- The user is the owner of the file or directory
3. In terms of file permissions, what do the following letters mean?
4. There are 4 pre-defined file permission levels in Windows NT. What are the names of the pre-defined levels?
5. Of the 4 pre-defined file permissions levels, what combination of file permissions make up each of the 4 levels? Hint: what combination of the choices in question #3 make up each of the 4 pre-defined levels?
6. When a NTFS partition is formatted or converted from a FAT partition, what are the default file permissions, and for what pre-defined Group(s)?
7. What are the 7 pre-defined directory-level permissions in Windows NT?
8. What is a potential system drawback to file and directory auditing?
9. To enable file or directory auditing, what selection under what menu command must be enabled in User Manager?
10. If file or directory auditing is enabled, where can one go (if they have the rights to do so) to check the auditing status, and at what log (of the 3 which Windows NT can maintain) do they need to specifically view?
11. A file named JUNK.TXT is on NTFS partition D, in a subdirectory named MAIL (hence, the file is in the D:\MAIL directory). The file has the permissions of RX (Read) for the group Everyone. What will happen to the permissions for this particular file in each scenario?
a. The file is copied to another subdirectory below D:\MAIL (for example, D:\MAIL\JUNE)
- The file inherits new permissions from the D:\MAIL\JUNE directory.
b. The file is copied to the root directory on partition D
- The file inherits new permissions present at the root directory level in partition D.
c. The file is renamed to OLDJUNK.TXT
- The file permissions do not change.
d. The file is moved to the root directory on partition D
- The file permissions do not change.
e. The file is moved to another partition on the same computer (for example, partition E)
- The file inherits new permissions present on the E partition.
12. Consider the following information:
There is a user account named "Famke" on a particular Windows NT machine. Famke belongs to 2 Groups; one group being "Actresses" and the other being "Models". Those 2 groups each have the following respective permissions for a given file named BOND.007
- Group Actresses permissions assigned for file BOND.007 --> Read
- Group Models permissions assigned for file BOND.007 --> Full Control
Famke also has the following permission assigned for BOND.007 --> Change
So, what are Famke's effective permissions for BOND.007?
- Read only
- Full Control
- Change
- No Access
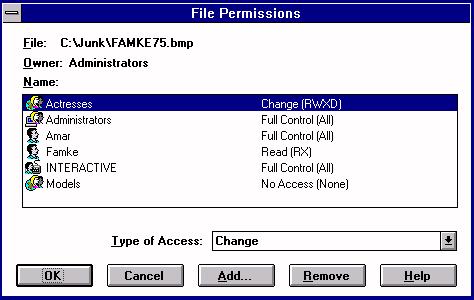
13. Given the information presented in the dialog box below, what are Famke's effective permissions for the file FAMKE75.BMP, and also considering that she is a member in the Actresses Group and the Models Group?

14. True or False:
a. Ownership of a given file can be taken, providing one has the proper access to do so.
- True
b. Ownership of a given file can be granted, providing one has the proper access to do so.
- False.
One may give another the permission to take ownership, but ownership cannot be explicitly granted -- it must be taken.
15. What are 5 backup methods that can be performed on a Windows NT Workstation?
16. What is the difference between an Incremental backup, and a Differential backup?
So what does this really mean??? When a file is backed up, typically the Archive bit (the "A" file attribute that one typically sees in File Manager, if all file details or file properties are being viewed) is cleared and one will not see an "A" next to that file. When the file changes (i.e. a time, date, or file size change due to a file modification or re-save), the Archive bit is flagged and set to "A" -- which is what you normally see in File Manager.
Hence, after a Normal backup (see question #15), a file's Archive bit is cleared (no "A"). When the file changes, the Archive bit is flagged and set to "A" for that file. If a Incremental backup is performed, that file is backed up because the "A" bit is seen as flagged, and then after the backup the "A" bit is cleared. On the other hand, if a Differential backup had been performed, the file is backed up because the backup program sees the file with the "A" bit flagged, however, the "A" bit is NOT cleared for that file.